|
R71 / MIEBACH |

|
 |
|
 |
CERN
|
SY
|
SY-EPC
|
HOME
|
CERN
|
SY
|
SY-EPC
|
HOME

|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| R71 | MIEBACH |
| Power In | 3 ~ 400V/630A |
| Power Out | 6400A/60V |
| Converter Type | Thyristors 12P |
| Control type | Local |
 Operation Responsibles
Operation Responsibles
| 1st Intervention |  Piquet SY-EPC Experimental Areas(163668) Piquet SY-EPC Experimental Areas(163668)
|
| Responsibles: | Yves GAILLARD |
| Xavier GENILLON |
 Power Converter Architecture
Power Converter Architecture
The R71 Power Converters are used in magnet workshops in buildings 151-R/002 and 867-R/C19 for DC and pulsed application.
This power converter is composed of 3 main parts:
The Power part contains the transformer,the Main Circuit Breaker, the thyristors bridge, the DCCT, the inductors and auxiliary circuitry.
The Power Supply Crate is integrated directly in the Power Converter enclosure. Its function is to provide the local interface between the Power Converter and the Converter Crate.
The Converter Crate is remotely located from the rest of the power converter components, in a rack close to the power part, to enhance the stability of the analog circuitry. Its function is to achieve with two loops the regulation of the output current and voltage.
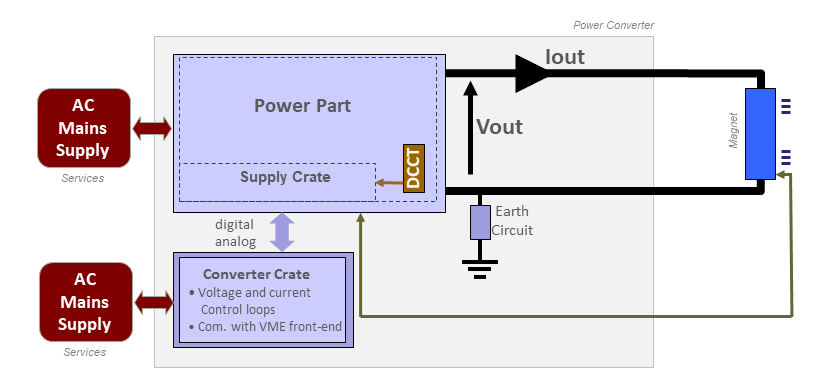
R71 power converter architecture
 Power Part
Power Part
The transformer has two primary delta windings and four secondary star windings
The secondaries each feeds a 3 single phase thyristor bridge assembly connected in parallel via a inductor.
The secondary circuits are protected against negative voltage with Free Wheeling diodes.The DC output is connected to the load via a DC ripple filter.
| Power In | 3 ~ 400V/630A |
| Power Out | 6400A/60V |
| Cooling type | Demineralized water |
| Converter Size | width: 3170mm |
| depth: 1250mm | |
| height: 2650mm |
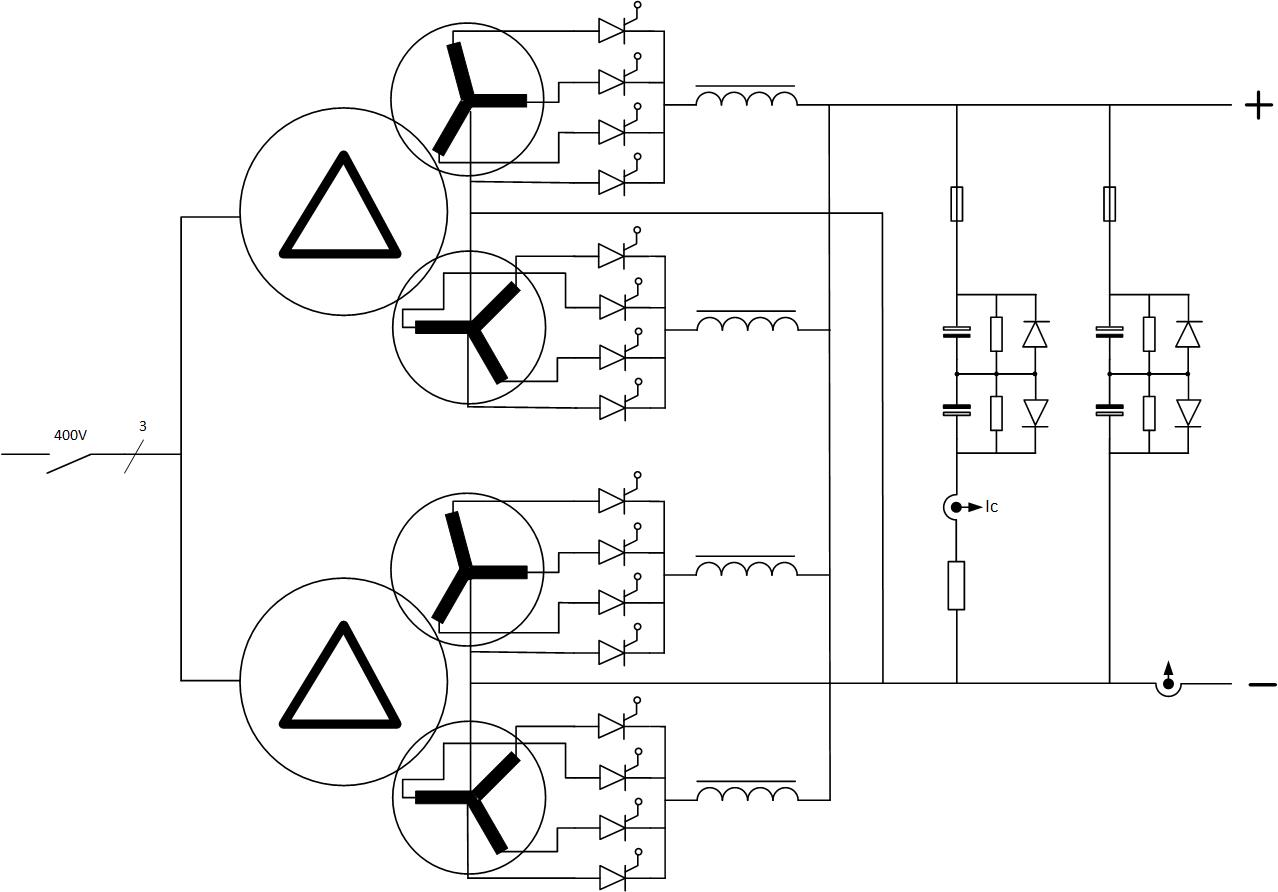
Power Part simplified Architecture / Topology .pdf
 Control & Regulation Part
Control & Regulation Part
Control: There is no remote control system. The operators use a external function generator to sent a current reference to the power converter. They use local commands to start and stop the equipment.
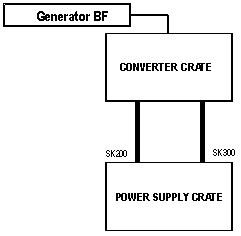
Control system simplified schematic
Regulation: Regulation of the output current and voltage is achieved with two loops, one for the voltage and one for the current. The voltage loop ensures fast correction of the output for perturbations on the incoming mains supply. The current loop ensures stabilisation for low frequency perturbations and has a variable integration time constant selection possibility. The voltage loop feedback is from a resistor potential divider network connected across the final output. The current loop is driven by a remote controlled precision reference source (DAC). A precision current transducer (DCCT) measures the output current and produces a voltage developed across high precision and stability resistors (burden). A precision comparator amplifier with very high gain, compares the DAC and DCCT signals and produces a voltage to drive the voltage loop of the regulator. The regulator circuit develops a control voltage (-5 to +7V) from the above two loops, to control the firing of the thyristor bridges. The firing of the thyristors in the bridge, which is synchronised with the 50 Hz incoming supply, occurs at a 300 Hz frequency. During operation such as Polarity Switch change and under fault circumstances, the Blocking signal acts directly on the Thyristor trigger drivers to inhibit the output firing circuits.
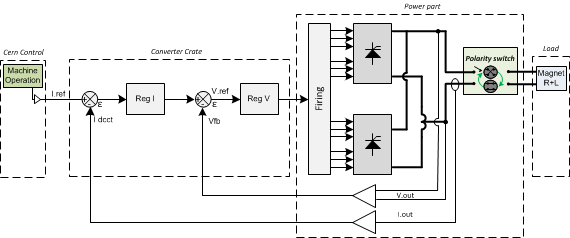
Regulation Control simplified schematic
 Magnet Protection
Magnet Protection
Each magnet connected to a North Area Power Converter can have a number of bits of feedback data for monitoring its status.
These can be as follows depending on the magnet involved:
- Water Pressure: This is a pressure sensor installed at the input of the cooling loop, integrated in the magnet. This alarm can also be triggered by a water flow sensor installed on some “Eletta” water cooled cables, which is wired in series with the magnet alarm. There is no separate alarm given.
- Water Temperature: This is a temperature sensor located at the exhaust side of the cooling loop.
- Coil Temperature: This is a series of temperature thermostats selected to protect the appropriate magnet against excessive coil temperature.
- Rheostat: This is no longer used, except to indicate a fault on the “Eletta” water cooled cables on GOLIATH magnet.
- Red Button: This is an “Emergency Off” switch located on the magnet to allow shut down of the associated Power Converter(s) in the event that someone working in the vicinity detects a fault. The Red Button alarm can also come, for selected Power Converters, from a contact on the Access System which is in series with the Red Button of the magnet.
- Terminal Box: This is a door interlock switch located on the second terminal box, installed between the Power Converter and the magnet. This interlock can be bypassed on the Power Control Crate by inserting a jumper on the front panel.(Safety procedures are affected by this action).
- Earth Fault: Monitor Earth current of the total circuit: converter + load (magnet and its DC cables), and take the right action if threshold reached. All four positive output points before the Polarity Switch are strapped together and connected to the Earth Leakage Protection sensor relay. Activation of the Earth Leakage sensor relay for either Power Converter will be indicated in the status data
Activation of any of the above signals automatically causes the “Stop” signal to be generated, causing the Reference Current value to go to zero, followed 30 seconds later with the switch off of the MCB, if the Polarity switch is not in the Stop position. This is initiated by the MCB Release signal.
 Magnet connection
Magnet connection

PS Main Magnet.
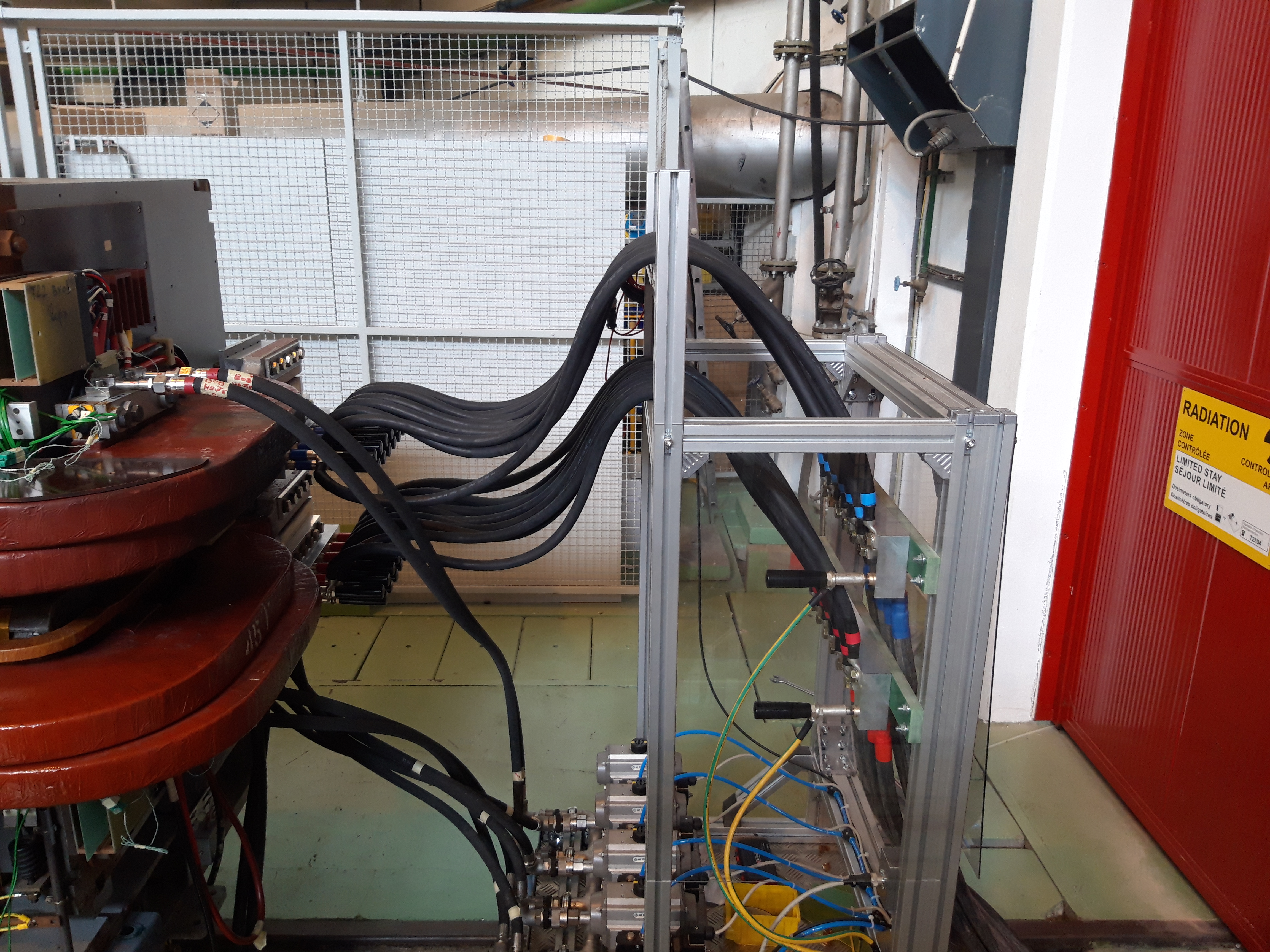
Magnet connection in bldg 151.
 Magnet Types
Magnet Types
R71 power converters supplies are used to test the PS main magnets and many others kind of magnets:
 Machine Installation
Machine Installation
Number of R71 power converters installed:
 Production Contract & Contract History
Production Contract & Contract History
- Manufacturer: MIEBACH
- Production year:
